Published on 2026-02-09

The journey from design for medical devices concept to market requires meticulous planning, strict compliance, and innovative engineering. Moreover, every step of the production process
must align with industry regulations and patient safety standards. A well-structured design for medical device processes ensures that products meet the highest quality benchmarks while adhering to regulatory requirements.
This article explores essential design principles and manufacturing strategies that contribute to developing high-quality, market-ready medical devices.
Table of Contents
Design for Medical Devices: Why Quality Design Matters in Healthcare
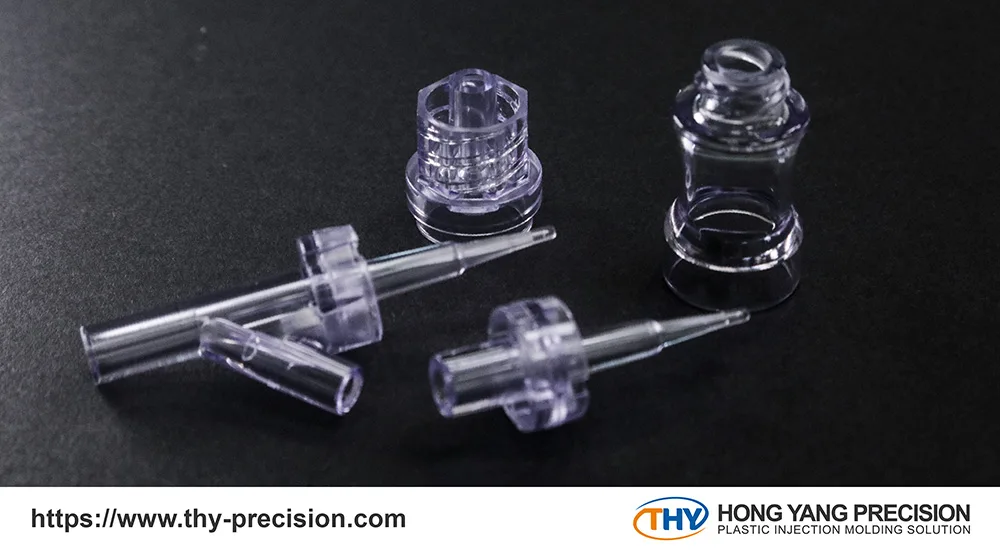

Medical device design is not just about aesthetics or functionality—it directly impacts patient safety, clinical outcomes, and regulatory approval. A poorly designed medical device can lead to serious complications, regulatory setbacks, and product recalls.
Design control refers to the systematic process of managing design and development activities. Regulatory agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) require manufacturers to establish and maintain a design control process to ensure consistency, quality, and risk mitigation throughout the device lifecycle.
The FDA’s 21 CFR Part 820.30 mandates manufacturers implement design controls in their Quality Management System (QMS) to ensure compliance.
Design for Medical Devices: From Concept to Market Launch
Bringing a medical device from concept to market is a rigorous and highly regulated process that requires careful planning, precise execution, and strict adherence to compliance standards. Below, we outline the key phases of the medical device manufacturing process.
1.Product Ideation
The development process starts with identifying an unmet medical need or an opportunity for improvement in existing medical devices. This phase involves market research, user interviews, and clinical observations. A well-defined product concept is critical to guide the design and development, reducing costly modifications later. Key considerations include:
- Identifying user needs: Engaging with physicians, surgeons, nurses, and patients to define the device’s purpose.
- Analyzing competitors: Reviewing existing products to identify gaps or limitations in the market.
- Establishing feasibility: Evaluating the concept’s technical, financial, and regulatory feasibility.
2.Classify the Devices
In the United States, the FDA oversees the manufacturing and distribution of medical devices, categorizing them into three classes based on risk levels. Class I devices (e.g., surgical gloves, bandages) are low-risk and require minimal regulatory oversight.
Class II devices, such as infusion pumps and diagnostic imaging equipment, pose a moderate risk and must meet stricter performance and labeling requirements. Class III devices, including pacemakers and artificial heart valves, carry the highest risk and undergo rigorous premarket approval (PMA) with extensive clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy.
3.Design Input
Design inputs serve as a blueprint for development, ensuring that each aspect of design for medical devices is carefully planned and aligned with its intended use. A key component of this process is material selection, which plays a crucial role in determining biocompatibility, durability, and sterilization compatibility.
In addition to material considerations, functional requirements are equally vital in shaping the device’s performance and reliability. These requirements define key attributes such as precision, power efficiency, software integration, and safety mechanisms, all of which must work seamlessly together to optimize device functionality.
For example, power needs directly impact the longevity of battery-operated medical devices, while software integration enhances automation and real-time monitoring capabilities.
4.Design Process
The actual design and development phase transforms the conceptual framework into functional prototypes, bringing the medical device one step closer to the market. This phase begins with creating initial sketches and CAD models to determine the device’s structural and mechanical design.
Once the basic design is established, prototyping techniques such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or injection molding are used to develop physical models for testing and refinement.
5.Design Output
Refined designs generate essential outputs that serve as a blueprint for production, ensuring regulatory compliance and manufacturing consistency. All design outputs must be traceable, well-documented, and stored within a QMS. Key design outputs serve as production blueprints, ensuring consistency in manufacturing, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
6.Verification and Validation
Once the design outputs are finalized, the medical device undergoes rigorous verification and validation (V&V) testing to ensure it functions as intended and meets real-world application needs. This phase is crucial for identifying potential issues early and ensuring the device performs reliably before entering production.
Verification ensures the device meets technical specifications, while validation confirms its effectiveness in real-world conditions.
7.Obtain Approval
After passing verification and validation, the device must obtain regulatory approval before it can enter the market. This process varies by region:
- FDA Approval (U.S.): For high-risk devices, a 510(k) clearance (for substantial equivalence) or a Premarket Approval (PMA) is required.
- CE Marking (EU): Requires compliance with MDR 2017/745 and approval from a Notified Body.
8.Market Launch
Once approval is obtained, the final phase focuses on scaling up production and bringing the device to market. Even after launch, manufacturers must comply with post-market surveillance regulations, monitor potential adverse events, and maintain adherence to safety and quality standards to ensure long-term reliability and patient safety.
Key Design Considerations for Modern Medical Devices
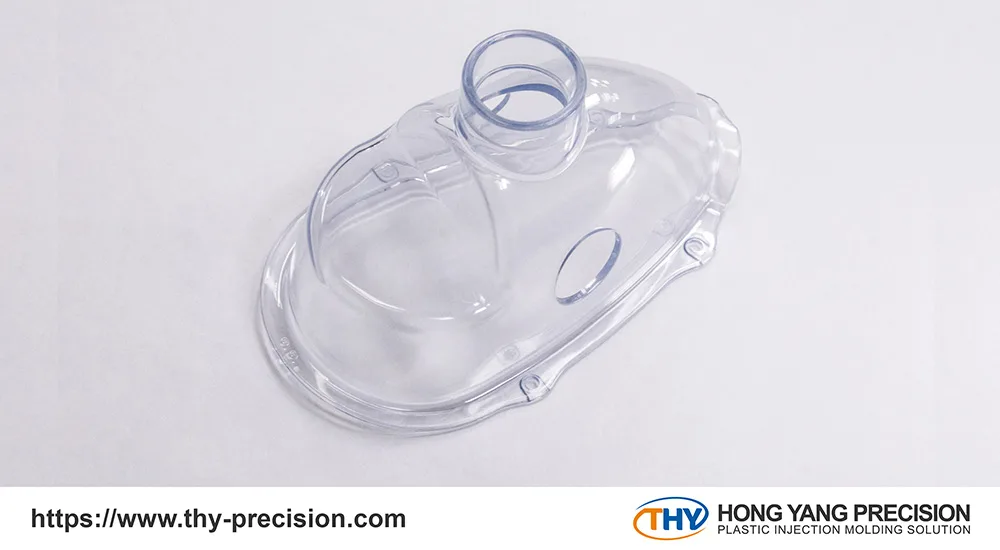

Here are five key design factors that significantly impact the performance and usability of medical devices.
1.Safety
Patient safety is paramount in the development of medical devices. Any failure or malfunction of a medical device can result in serious health risks. Key safety considerations include:
- Biocompatibility
Materials used in medical devices must be non-toxic, non-carcinogenic, and non-reactive to human tissue. Adherence to ISO 10993 ensures that the materials used do not cause adverse biological reactions.
- Electrical and mechanical safety
Devices with electrical components must comply with IEC 60601-1, the international standard for the safety of medical electrical equipment. This standard covers insulation, leakage current, and protection against mechanical hazards.
- Sterilization and infection control
Reusable medical devices, such as surgical tools and diagnostic probes, must be designed for easy sterilization without compromising material integrity. Compliance with sterilization standards such as ISO 17664 is essential.
- Fail-safe mechanisms
Devices should be equipped with redundant systems, emergency shut-offs, and alarms to prevent critical failures.
Manufacturers can more efficiently reduce risk by incorporating safety measures from the early design stages and ensuring regulatory approval.
2.Traceability
In medical device design, traceability ensures quality control, regulatory compliance, and post-market surveillance by tracking each component throughout its lifecycle. A robust traceability system improves audit efficiency, enhances quality control, and enables swift product recalls when needed.
Key elements include:
- Unique Device Identification (UDI)
Global regulations mandate unique serial numbers for tracking. (e.g., FDA’s UDI, EU’s MDR) - Design History File (DHF)
This file documents the design process and ensures compliance with ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
- Device Master Record (DMR)
Contains manufacturing specifications to ensure consistency with design. - Post-Market Surveillance (PMS)
Monitors device performance, malfunctions, and customer feedback for safety.
3.Ultra-Low Power
Refined designs generate essential outputs that serve as a blueprint for production, ensuring regulatory compliance and manufacturing consistency. Energy efficiency is crucial for medical devices, enabling longer battery life, reduced maintenance, and enhanced patient comfort.
4.Risk Management
Risk management is essential in medical device development, ensuring safety and regulatory compliance. The design for medical devices must incorporate the ISO 14971 standard, which provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks.
Key strategies include:
- Hazard Identification
Conducting Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to detect potential failures. - Mitigation Strategies
Addressing risks through design changes, software updates, or safety features. - Human Factors Engineering
Reducing user errors with intuitive design, clear labeling, and ergonomic considerations.
5.User-Centered Design
Medical devices should prioritize user-centered design, ensuring accessibility, ease of use, and inclusivity. A well-designed device improves patient adherence, reduces errors, and enhances clinical outcomes.
Key user-centered design principles include:
- Accessibility
Devices must be easy to use, even for patients with limited dexterity, vision impairments, or cognitive challenges. - Inclusivity
Designs should accommodate diverse users, considering age, gender, body size, and mobility limitations. - Human Factors Engineering (HFE)
FDA and ISO 62366 emphasize usability testing, ergonomic design, and real-world simulations.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Partner: Ensuring Quality and Market Competitiveness
Selecting the proper medical component manufacturer is crucial for regulatory compliance, production efficiency, and product reliability. Companies should evaluate potential partners based on key factors such as certification, regulatory expertise, comprehensive solutions, and cleanroom capabilities.
1.Does the Manufacturer Hold ISO Certification?
ISO 13485 certification ensures adherence to international quality and safety standards. Certified manufacturers maintain well-documented processes, guaranteeing compliance and product reliability.
2.Does the Manufacturer Have Expertise in Regulatory Compliance?
Medical device manufacturing requires deep knowledge of global regulations, including FDA 21 CFR Part 820, EU MDR (2017/745), and ISO 13485. A partner with regulatory expertise reduces compliance risks, prevents costly redesigns, and accelerates market approval.
3.Does the Manufacturer Offer Comprehensive Solutions?
A full-service manufacturing partner optimizes production by integrating multiple processes, eliminating the need for multiple vendors. Their key offerings include design for manufacturability (DFM), rapid prototyping, strategic material selection, and a seamless transition from initial concept to full-scale production.
4.Does the Manufacturer Operate in a Cleanroom Environment?
Contamination control is essential in medical device production. Manufacturers should comply with ISO 14644 cleanroom standards, ensuring sterility and regulatory compliance while minimizing contamination risks.
A reliable manufacturing partner enhances competitiveness and ensures that medical devices meet the highest safety, performance, and quality standards.
Why Choose Us? Excellence in Medical Device Manufacturing
At THY Precision, we specialize in medical device manufacturing, ensuring every product meets global safety and performance standards. Our ISO 13485-certified processes and ISO 8 cleanroom environment guarantee strict quality control and regulatory compliance, preventing contamination and ensuring medical-grade safety.
With over 40 years of expertise in precision machining, component assembly, and plastic injection molding, we offer customized solutions for small-batch prototyping and large-scale production. Ready to bring your medical device to market? Contact us today!
Learn more
Medical Device Implants: What You Should Know
IV Set Components: Essential Parts and Their Roles in Healthcare
